Radio Quasar 3C263
Description
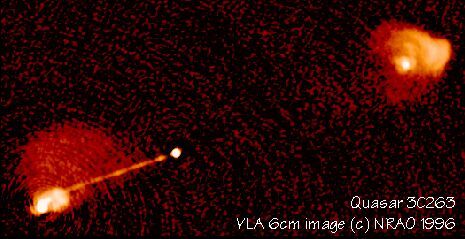
This image shows the radio emission from relativistic streams of high energy particles generated by the quasar. This is a classic double-lobed radio source. Astronomers believe that the jets are fueled by material accreting onto a super-massive black hole at the center of the host galaxy (not shown in this image). The high energy particles are confined to remarkably well collimated jets, and are shot into extragalactic space at speeds approaching the speed of light, where they eventually balloon into massive radio lobes. The overall linear size is 200/h kpc (Hubble constant H = 100h km/s/Mpc). The quasar has double lobes with prominent hot spots, and has a narrow jet, but no counter-jet. It is possible that we only see the jet that is pointing toward us, which may be "Doppler boosted" in brightness when the particles emitting the radio radiation are moving toward us at close to the speed of light. The counter-jet would be moving away from us, and would thus not experience Doppler boosting. Within the nuclear radio source, features have been seen which appear to be moving at speeds faster than the speed of light. This apparent "superluminal motion" is an illusion that happens when the emitting material is moving at velocities close to, but less than, the speed of light and in a direction very close to our line of sight. Under these conditions, the signal from plasma clouds which emit their radiation later in time has less distance to travel than material which was emitted earlier, and the signal appears to arrive at the telescope in less time than the light travel time between the two regions.
FR II quasar at z=0.646. VLA 4.9 GHz image at 0.36 arcsec resolution.
Creator
Legacy Astronomical Images
Rights
NRAO/AUI/NSF does not hold full copyright for this image. Contact the archivist for details.
Type
Legacy Astronomical Image
Object Name
3C263
Investigators
Alan H. Bridle, David H. Hough, Colin J. Lonsdale, Jack O. Burns, Robert A. Laing
Telescope
Very Large Array (VLA)
Observation Date
1987-07-11
Type of Observation
continuum
Band
C
Wavelength
6 cm
Frequency
5.0 GHz
Center of Image
RA 11:39:57.000, Dec: 65:47:49.500 (J2000)
Field of View
0.200000 x 0.300000 degrees
Link to journal article
Series
Active Galactic Nuclei Series
Unit
Quasars Unit
Citation
Legacy Astronomical Images, “Radio Quasar 3C263,” NRAO/AUI Archives, accessed June 13, 2025, https://www.nrao.edu/archives/items/show/33347.